Indoor air quality: the impact of CO2 on health and well-being at work
According to a study by the OQAI, indoor air is on average 5 to 7 times more polluted than outdoor air, even though we spend 80 to 90% of our time indoors, mainly in our workplace. This is due to many factors and pollutants that can have an impact on our health. To name but one, CO2, which is one of these factors, very present in buildings.
Reading time : 10 minutes
CO2, a greenhouse gas
CO2 is the fourth most present gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, representing 77% of greenhouse gas¹ (GHG) emissions. It is a colorless, odorless and harmless gas in a normal concentration range.
There are two types of CO2 concentration:

- The concentration of CO2 emitted by human activities :
Mainly caused by the use of fossil fuels (oil, gas, coal) and land use change (agriculture and deforestation). Moreover, it is produced by the transport sector, industry and housing. These emissions increase the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, and consequently increase global warming.

- The concentration of CO2 emitted by human respiration:
The latter has no impact on global warming, unlike human activities. In indoor air, the concentration of CO2 is used as an indicator of the level of air confinement since it is extremely dependent on human occupation and air renewal in the building or room.

It is measured in ppm (parts per million) or µg/m3. Indoor CO2 levels are generally higher than outdoor levels due to CO2 exhaled by occupants. It should be noted that there can be harmful impacts when concentrations are higher than about 1000 ppm such as health risks and reduced work efficiency.
Indoor Carbon dioxide and its impact on the health of occupants?
According to ANSES, the level of carbon dioxide in the indoor air of buildings is usually between 350 and 2500 ppm.
The ANSES recommends to schools and other public places, a sufficient renewal of air to avoid exceeding 1000 ppm. Which is the maximum accepted concentration of carbon dioxide in the air.
Indeed, an exposure of only 1000 ppm is enough to notice harmful effects and can lead to more serious consequences on health, especially if the exposure to the recommended CO2 concentrations is not respected.

Air polluted by CO2 consequences
As can be seen in the table above, high exposure to CO2 have negative effects on the efficiency and productivity of employees, and on their health. It proved that good air quality with controlled confinement improves cognitive abilities and reduces absenteeism.
CO2 and SARS-COV-2
Monitoring the air quality of a room has become essential to limit the spread of COVID-19 in work spaces and establishments gathering the public.
The HCSP (High Council for Public Health) and the Ministry of Labor, have updated their version of the health protocol in companies and asked each employer to measure the good quality of the air to insure that the carbon dioxide level is accepted.
Indeed, according to recent expert reports from the HSCP and INRS, the control of Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is an essential element of prevention to reduce the risk of transmission.
To minimize the risk of airborne transmission of viruses, CO2 levels should be as possible in all indoor spaces. It is recommended to stay close to 400 ppm, (outdoor CO2 concentration), and below 800 ppm. If the threshold is exceeded, it is recommended to leave the room and to renew the air.
How to improve indoor air quality and the impact of CO2?
The managers of establishments are required by law and must take into consideration the atmosphere in which the occupants are. In addition to respecting the policy of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), worrying about the quality of indoor air in companies is required to optimize the working environment and act positively on the Quality of Life at Work (QWL).
To ensure the health and comfort of people present in institutions – in companies as in schools – there are several ways to analyze the rate of CO2 :
- Air the rooms: it is recommended to open the windows and the doors regularly to reduce the effects of confinement.
- Have a good ventilation: an efficient ventilation system is recommended to ensure a good air renewal.
- Controlling pollution sources: there are many sources of pollution and it is important to limit them. It is essential to choose the furniture carefully, to use “healthy” cleaning products or to isolate the photocopiers etc. More information here.
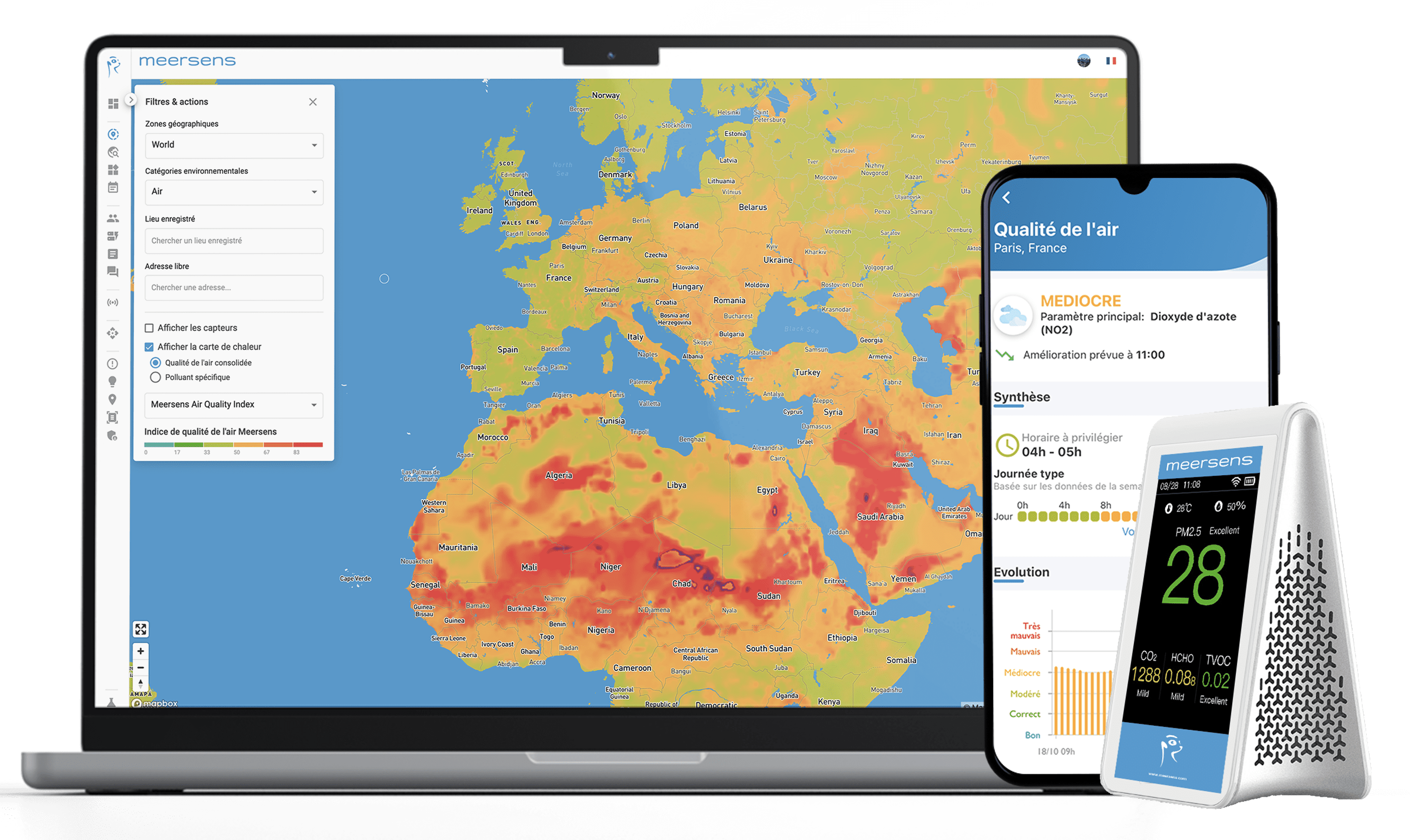
- Take measurements using air quality sensors: these sensors measure the carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants levels in the room to take the right decisions and apply adapted corrective measures.
Meersens proposes the deployment of sensors to monitor data related to indoor air quality in buildings. With these sensors, it is possible to know in real time the temperature, humidity, fine particles, gases (CO2, VOCs) …
These data can then be found on our monitoring platform Meersens and keep a history.
We make the invisible visible to protect your resources and mitigate risks, thus ensuring the health and comfort of populations.






mostbet сабти ном хато https://mostbet43926.help/
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# canadian pharmacy 24h com safe
Koszykowka https://koszykowkanews.pl najnowsze wiadomosci, PLK, transfery i wyniki meczow. Sledz polska lige, turnieje miedzynarodowe i postepy zawodnikow, dowiedz sie o transferach, statystykach i najwazniejszych wydarzeniach sezonu.
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article.
I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the
post. I will definitely return.
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# best rated canadian pharmacy
https://vetfreemeds.com/# online pet pharmacy
Spirit of the Aerodrome Hub – The posts are presented in a way that makes learning effortless.
Everything about FC Qarabag https://qarabag.com.az in one place: match results and schedule, Premier League standings, squads and player stats, transfers, live streams, and home ticket sales.
IDMAN TV https://www.idman-tv.com.az live stream online: watch the channel in high quality, check today’s program guide, and find the latest TV schedule. Conveniently watch sporting events and your favorite shows live.
Free online games http://www.oyun-oyna.com.az/ with no installation required—play instantly in your browser. A wide selection of genres: arcade, racing, strategy, puzzle, and multiplayer games are available in one click.
Watch Selcuksport TV http://www.selcuksports.com.az/ live online in high quality. Check the broadcast schedule, follow sporting events, and watch matches live on a convenient platform.
Julie Cash juliecash online on OnlyFans features exclusive content, private posts, and regular updates for subscribers. Subscribe to gain access to original content and special offers.
Nice blog here! Additionally your website a lot up very fast!
What host are you the use of? Can I get your affiliate link to your host?
I wish my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Lily Phillips https://lily-phillips.com offers unique intimate content, exclusive publications, and revealing updates for subscribers. Stay up-to-date with new content, access to original photos, and special announcements on her official page.
Unique content from Angela White angelawhite.ing new publications, exclusive materials, and personalized updates. Stay up-to-date with new posts and access exclusive content.
Shilpa Sethi shilpasethi in official page features unique, intimate content and premium publications. Private updates, fresh photos, and personal announcements are available to subscribers.
Brianna Beach’s exclusive briannabeach page features personal content, fresh posts, and the chance to stay up-to-date on new photos and videos.
Riley Reid riley reid is a space for exclusive content, featuring candid original material and regular updates. Get access to new publications and stay up-to-date on the hottest announcements.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
Google salaries by position https://salarydatahub.uk comparison of income, base salary, and benefits. Analysis of compensation packages and career paths at the tech company.
Sabrina Cortez sabrina cortez offers unique content and fresh publications. Join us on social media to receive exclusive updates and participate in exciting activities.
Exclusive content Alexis Fawx alexisfawx.online original publications and special updates. Follow us on social media to stay up-to-date on new releases and participate in exciting events.
Любишь азарт? pinap онлайн-платформа с широким выбором слотов, настольных игр и живого казино. Бонусы для новых игроков, акции, турниры и удобные способы пополнения счета доступны круглосуточно.
Bunny Madison bunnymadison features exclusive, intimate content, and special announcements. Join us on social media to receive unique content and participate in exciting events.
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – canadian pharmacy near me
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
My Mexican Pharmacy: mexico drug store – pharmacy delivery
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – canada pharmacy 24h
Scarlett Jones http://www.scarlettjones.in shares exclusive content and the latest updates. Follow her on Twitter to stay up-to-date with new publications and participate in exciting media events.
Discover Avi Love’s https://www.avilove.online world: exclusive videos, photos, and premium content on OnlyFans and other platforms.
Die Welt von Monalita https://monalita.de bietet exklusive Videos, ausdrucksstarke Fotos und Premium-Inhalte auf OnlyFans und anderen beliebten Plattformen. Abonniere den Kanal, um als Erster neue Inhalte und besondere Updates zu erhalten.
https://certicanpharmacy.shop/# CertiCanPharmacy
Полная статья здесь: оборудование ситуационных центров
Dive into the world of Dolly Little https://www.dollylittle-official.online original videos, exclusive photos, and unique content available on OnlyFans and other services. Regular updates and fresh publications for subscribers.
Discover the world of LexiLore lexilore ing exclusive videos, original photos, and vibrant content. Regular updates, new publications, and special content for subscribers.
Serenity Cox http://www.serenitycox.ing shares exclusive content and regular updates. Follow her on Instagram, Twitter, and Telegram to stay up-to-date on creative projects and inspiring events.
My Mexican Pharmacy: pharmacy mexico city – My Mexican Pharmacy
Get to know JakKnife jakknife online and discover unique content. Regular updates, special publications, and timely announcements are available to subscribers.
Discover the world of Comatozze https://comatozze.in exclusive content on OnlyFans and active updates on social media. Subscribe to stay up-to-date on new publications and exciting projects.
The official website of MiniTina http://www.minitinah.com your virtual friend with exclusive publications, personal updates, and exciting content. Follow the news and stay connected in a cozy online space.
Karely Ruiz https://karelyruiz.mx/ comparte contenido exclusivo y actualizaciones periodicas. Siguela en Instagram, Twitter y Telegram para estar al tanto de sus proyectos creativos y eventos inspiradores.
водопонижение иглофильтрами грунтовых вод водопонижение иглофильтрами грунтовых вод .
водопонижение иглофильтрами москва водопонижение иглофильтрами москва .
https://vetfreemeds.com/# pet meds official website