Carbon dixoide (CO2) : sources of pollution and health impacts
Carbon Dioxide (or CO2), naturally present in the air, can be dangerous to health if it reaches significant quantities in the air we breathe. But what is it exactly? What is the source? What are the impacts?
Reading time: 4 minutes
Summary
What is carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Carbon dioxide (CO2), what are the sources?
What are the environmental and health impact of carbon dioxide?
How to protect yourself and reduce dixoyde carbon (CO2) emissions?
What is carbon dioxide (CO2)?
Carbon dioxide isn’t considerate like an air pollutant, because it is naturally present in the air.
CO2 is a natural gas, composed of one carbon molecule and two oxygen molecules.
It is colorless and painless and it can be dangerous to health if it reaches significant quantities in the air we breathe.
Carbon dixoide (CO2) : what are the sources?
CO2 can comme from different sources : natural or human.
🏭 Outdoor sources
Outdoor, carbon dioxide is produced mainly by human activities that release 25 billion tons of CO2 per year into the atmosphere ((oil combustion contributes 35.2%, coal 32% and natural gas 12.8%. The remaining 20% is produced during the massive clearing of the equatorial forests)¹
🏠 Indoor sources
Inside, carbon dioxide comes from outdoor CO2, human respiration and internal combustion sources (wood stove, gas heating for example…).
Its concentration in the indoor air of buildings is often higher than outside because the air circulates less well.
The latter is an indicator of the level of air confinement.
Carbon dioxide (CO2): impacts on health and the environment
💙 The impact of CO2 on health
Outside, CO2 has no impact on human health.
High level of CO2 inside buildings can have consequences on health, work efficiency. and sleep. It is a matter of great importance for offices, schools and domestics environments.
It is recommended that the average exposure of a person over a continuous period of 8 hours should not exceed 5000 ppm.
An exposure of only 1000 ppm is enough to ntice harmful effects (headaches, dizziness, fatigue…) and this can lead to more serious health consequences (breathing difficulties, increased heart rate, asphyxiation…) if the exposure to the recommended CO2 concentrations aren’t respected.
Short-term effects
👉Maux de tête
👉 Inconfort olfactif
👉 Irritation de la peau et des muqueuses
👉 Fatigue
👉 Toux, respiration douloureuse
👉 Pneumonie, bronchite
Long-term effects
👉Le système nerveux central est altéré (maux de tête, anxiété)
👉 Maladies cardiovasculaires
👉 Maladies respiratoires (asthme)
👉 Cancers
👉 Impacts sur le foie, la rate, le sang
👉 Impacts sur l’appareil reproducteur
🌍 The impact of CO2 on the environment
Carbon dioxide (or CO2) is often mentioned when we talk about environment.
However, CO2 gas should not be confused with CO2 equivalent (or eq-CO2).
💡 Good to know : The CO2-eq is a unit created by the IPCC to compare the impacts of these different GHGs on global warming. It is a simplified tool that allows the identification of priority actions to fight against global warming and is notably necessary to set up carbon markets². To summarize, CO2 is a greenhouse gas while the eq-CO2 is a unit of conversion of the different greenhouse gases.
Increasing the concentration of CO2 improves yields in agriculture. Plants use CO2 during photosynthesis. With an increase in the concentration of CO2 their growth is stimulated and therefore their yields are better.
However, the global warming in which CO2 participates also leads to an increase in temperatures and extreme weather conditions that cause damage to crops. Moreover, even if the increase in yield is noted, it results in a loss of quality (degraded nutrient content for wheat for example). The quantity is therefore at the expense of quality.
How to protect yourself and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions?
🏭 Reduce outdoor CO2 emissions
To reduce outdoor CO2 emissions and limit global warming and its devastating impacts, the IPCC lists in its report several scenarios with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality (zéro CO2 emission) by the early 2050s.
👉 Improve the energy transition
By shifting the maximum amount of electricity and heat production to low-carbon sources, such as renewable energy or nuclear power.³
👉 Transform our modes of transport
Road transport is one of the largest emitters of CO2 on the planet, ahead of air and sea transport.
👉 Enhance our agriculture
Agriculture emits nearly 15% of the world’s CO2 emissions, to which we must add deforestation.
🏠 Reduce indoor CO2 emissions
To improve indoor air quality in buildings and reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2), it’s recommended:
👉 Improve ventilation and filtration
Simply replace the air filters of the ventilation systems regularly.
👉 Install indoor air quality sensors
Installation of air quality sensors allows continuous measurement of the CO2 level inside a house or building.
👉 Open the windows
The outdoor CO2 concentration is between 410 and 500 ppm, lower than the indoor air.
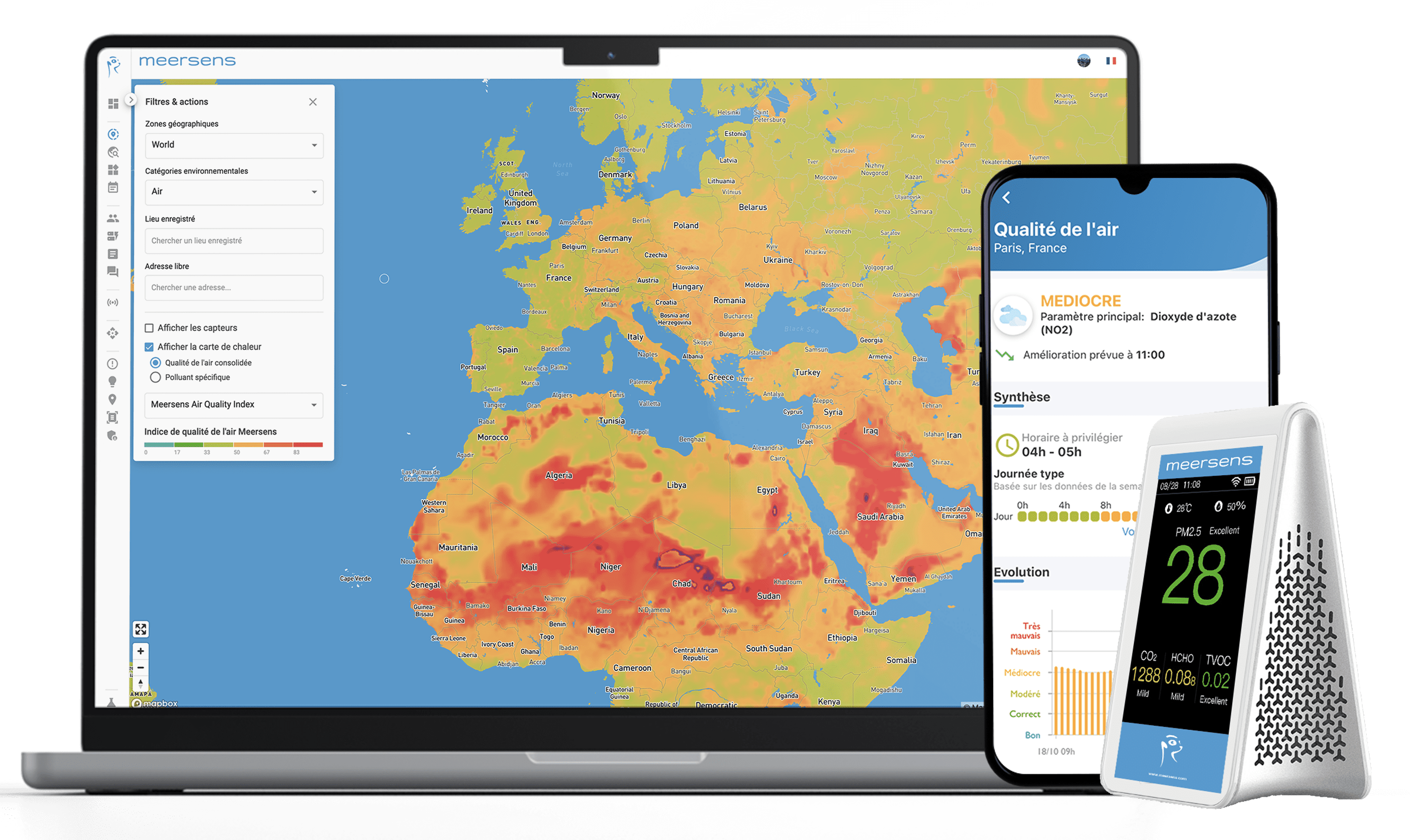
To monitor outdoor air pollution and especially carbon dioxide (CO2), Meersens allows you to analyze the environment wherever you are, whenever you want thanks to the power of environmental intelligence.
Meersens’ modeling and our easy-to-deploy air quality sensors allow to know the concentration of CO2, in real time and anywhere in the world to ensure the health and well-being of populations.
Are you confronted with high CO2 concentrations?
Meersens analyze the quality of your environement
Meersens is a positive impact environmental health company, mobilized to create a sustainable future, enabling environmental risk mitigation and positively contributing to the health and well-being of stakeholders – by providing customized environmental monitoring and prevention.
Meersens provides 360°, real-time, historical and predictive multi-pollutant monitoring and insight for any location with high accuracy, enabling you to mitigate risks and make better decisions.







mexican pharmacies that ship: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
canadian pharmacy drugs online CertiCanPharmacy canadian pharmacy service
canada pet meds: VetFree Meds – pet pharmacy online
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# pet pharmacy
pet prescriptions online: dog medicine – pet pharmacy online
medicine from mexico: My Mexican Pharmacy – pharmacy in mexico that ships to us
pet meds official website: pet pharmacy – pet pharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
pet drugs online: discount pet meds – dog medicine
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# pet pharmacy
My Mexican Pharmacy: mexico prescriptions – My Mexican Pharmacy
My Mexican Pharmacy mexico pharmacy My Mexican Pharmacy
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# order from mexico
progreso mexico pharmacy online: the purple pharmacy mexico – mexico meds