Ozone (O3): sources and health impacts
Every summer, during hot weather or heat waves, the ozone pollution alert is never far away. Ozone: a pollutant that is both a source of life and death: a question of altitude.
Reading time : 4 minutes
Summary
What is ozone?
What are the sources of ozone?
What are the dangers of ozone?
What to do in case of ozone (O3) pollution peaks
How to reduce and measure ozone?
What is ozone?
There are two types of ozone:
Stratospheric ozone
Also known as the “ozone layer”. It is called the “good” ozone because it will form a protective layer in the stratosphere (i.e. between 10 and 50km above sea level) and absorb ultraviolet (UV) rays that can be harmful to human health. Ozone in the Earth’s stratosphere represents 90% of the concentration. It is destroyed by aerosols, notably from human activity, including CFCs, thus causing a hole in the ozone layer.
Tropospheric ozone
Or “bad ozone”, is a greenhouse gas (GHG), an air pollutant and a major component of photochemical smog.The latter forms a layer located in the troposphere (i.e. at an altitude of less than 10km). It can be recognized by its bluish color and pungent odor. Tropospheric ozone is formed by photochemical reactions of other pollutants and is generally present for a short period of time.
How is ozone (O3) formed?
Ozone (O3) is a so-called “secondary” pollutant, i.e. it is not released directly into the atmosphere and is not released directly by human activities. The high temperatures and the strong luminous radiation will support the chemical reactions in the low layers of the atmosphere producing ozone from the following primary pollutants:
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx) mainly from road traffic,
- The Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) which come from several sources and mainly: solvents and paints, industries, road traffic (mainly two wheels) and plants.
It is triggered by solar radiation, which is why ozone concentrations are more present in summer and during the day – often between May and September.
Most of the ozone found inside buildings comes from outdoor sources. It is estimated that the indoor ozone concentration is about half the concentration measured outdoors.
O3 concentrations can be found in poorly ventilated spaces, in offices where there are old photocopiers or laser printers. The latter, if they are recent, have an “ozone filter” which destroys the ozone formed and allows to limit the emissions to a minimum.

The right gestures : since the highest concentrations of ozone (outdoors) are found between 12 noon and 8 p.m., it is advisable, during ozone episodes, to air the rooms in the home outside this time frame
The dangers of ozone (O3)
💙 Health effects of ozone (O3)
According to a report by Ademe, 21,400 deaths per year due to ozone pollution, which results from a reaction of nitrogen oxides and volatile compounds emitted into the atmosphere, particularly by road traffic.
Ozone compared to fine particles is still responsible for fewer anticipated deaths each year, but this is no reason to neglect its impact on health and the environment.
Ozone (O3) is an irritating gas that, at high concentrations, can penetrate to the respiratory tract and cause serious health problems.
🟠 Concentrations that exceed 180 µg/m3 on an hourly average are especially dangerous for children, the elderly, respiratory patients, and asthmatics because they are particularly sensitive to ozone pollution.
🔴 From 240 µg/m3, there is a high risk for the whole population. Thus, intense physical effort outdoors should be avoided during periods of high ozone concentrations.
The effects of ozone on human health are characterized by coughing, eye, nose and throat irritation, headaches, shortness of breath, chest pain up to decreased lung function, triggers for asthma attacks and more severe respiratory symptoms.
During the summer months, a significant presence of ozone can also increase awareness of pollens.
🌏 Effects of ozone (O3) on the environment
That’s not all, this gas is also dangerous for the environment since at high levels, ozone:
👉 Contributes to the acidification of air, surface water and soil
👉 Disrupts ecosystems (affects the process of photosynthesis, forest dieback, acidification of freshwater lakes, damage to the food chain…)
👉 Decreases crop yields
👉 Degrades materials (rubber), buildings and crops
👉 Contributes to the greenhouse effect responsible of global warming
What to do in case of ozone (O3) pollution peaks?
In the event of an ozone peak, it is advisable to avoid going out in the afternoon and engaging in intense physical or sporting activities outdoors (postpone your running trips to the end or beginning of the day).
Moreover, be vigilant to the state of health of sensitive people (pregnant women, children, elderly people, asthmatics…), air your interior at the beginning or end of the day. In case of respiratory or cardiac discomfort, consult a health professional.
How to reduce and measure ozone (O3)?
The fight against ozone pollution is a major issue in the field of air quality, given the impact of this pollution on human health and the environment.
European thresholds and target values for ozone
The directive on air quality and clean air for Europe (2008/50/EC), transposed into French regulations, sets :
🟡 An information and recommendation threshold at 180 µg/m3 as an hourly average
🔴 An alert thresholdat 240 µg/m3.
The European Union has defined an overload indicator for the protection of vegetation: the « AOT40 » (= Accumulated Ozone over Threshold of 40 ppb (80 µg/m3)). This indicator is intended to protect crops and (semi)natural vegetation. The European target value is 18000 (µg/m³).h., averaged over 5 years. The long-term objective is 6000 (µg/m³).h.
In France, two indicative occupational exposure limit values (OELVs) have been published for ozone. The maximum exposure value for ozone in the workplace is set at 200 µg/m³ or 0.1 ppm (8-hour average value).
See all air quality guidelines here.
Taking action and protecting yourself in the short term on ozone
Ozone is chemically produced in the atmosphere by the reaction of pollutants emitted by human activities with solar rays. It is possible to limit its formation by reducing the concentration of primary pollutants at the origin of its formation. For that it is advised:
👉 Observe speed limits or evenlower your speed by 20 km/h as this will decrease the production of NOx, SOx, and VOCs,
👉 To avoid driving with vehicles that may not comply with the standards for Crit’air stickers adequate on days of announced pollution peaks, in order to avoid too much NOx and SOx emission,
👉 To favor modes of travel such as biking, walking or public transportation,
👉 To limit activities known to emit pollutants such as VOCs, SOx, NOx,
👉 To Avoid chemicals such as solvents or paints as much as possible.
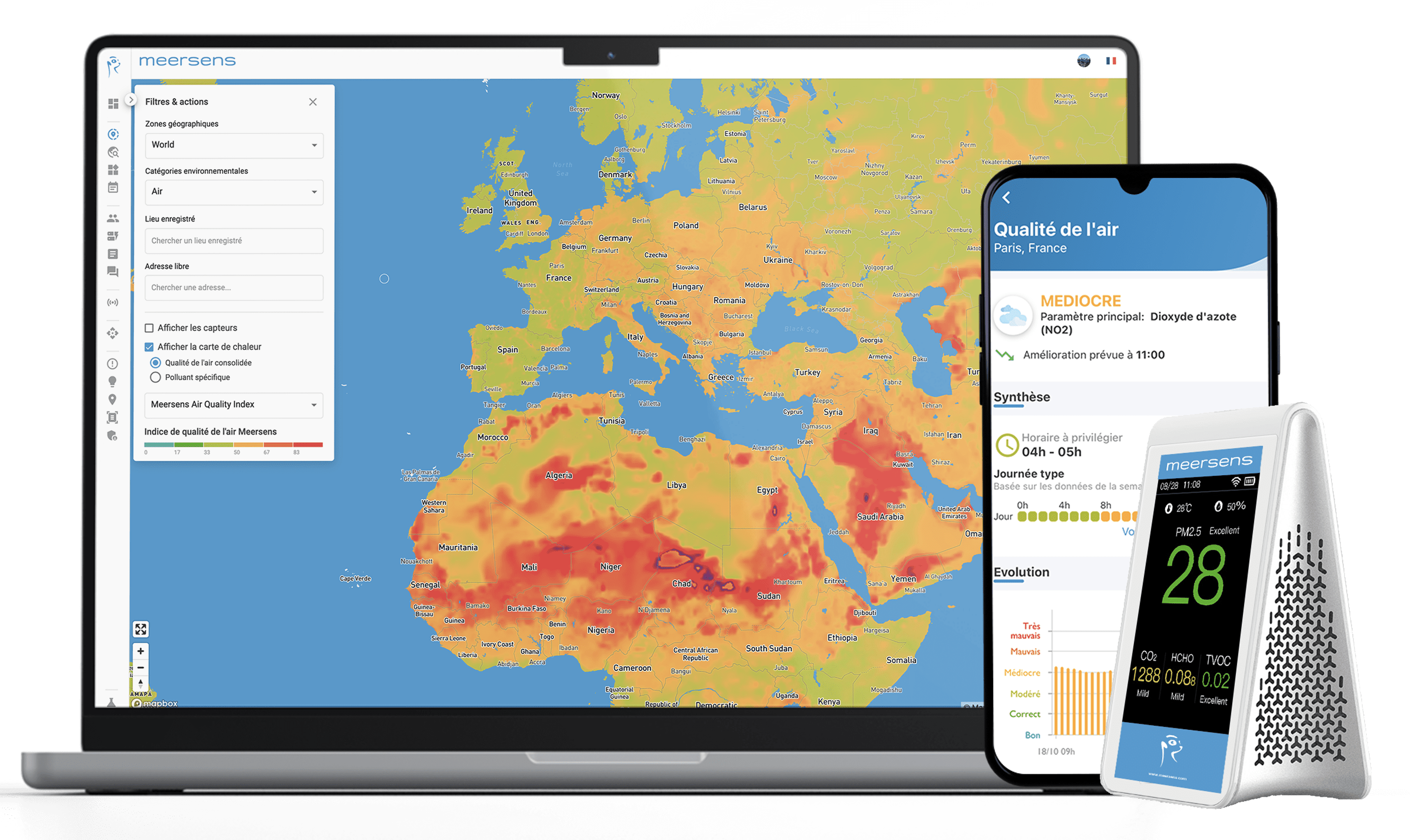
Measuring and monitoring ozone with Meersens solutions
In summer, many areas of France are affected by ozone pollution. This is the case for example in the Rhône Alpes region and particularly in the Grenoble basin, in the Arve Valley, which concentrates all human activities in a narrow space, and in large cities such as Paris or Marseille. Il est donc urgent d’agir sur les quantités d’ozone, que ce soit dans les villes, dans les entreprises ou encore dans les écosystèmes de santé !
Meersens’ modeling and our easy-to-deploy air quality sensors allow us to know the concentration of ozone (O3), at street level (10mx10m), in real time and everywhere in the world, indoors and outdoors.
We also have the capacity to monitor other pollutants, including nitrogen dioxide (NO2), particulate matter (PM2.5,10…), carbon monoxide (CO), and many more, thanks to our multi-platform solution.
Contact us today to make the world, a safer and more sustainable place, while taking care of your stakeholders.






This is a topic that is close to my heart… Best wishes! Life Experience Degree
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
dog medicine: best pet rx – pet rx
real canadian pharmacy: canada pharmacy online legit – canadian pharmacy store
My Mexican Pharmacy [url=https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/#]My Mexican Pharmacy[/url] My Mexican Pharmacy
canada pharmacy world: pharmacy rx world canada – legitimate canadian pharmacies
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# mexico prescriptions
canadian pharmacy 365: CertiCanPharmacy – CertiCanPharmacy
https://certicanpharmacy.shop/# CertiCanPharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# vet pharmacy online